ON THE WALL NEXT to one of the several gates, the Daulat Prole, that leads into the Junagarh Fort in Bikaner, you can see a set of what look like the impressions made by pressing hands into a soft material. Each of these hand prints is labelled in Hindi (Devanagari) lettering. These impressions are amongst the last actions of widows about to commit sati.
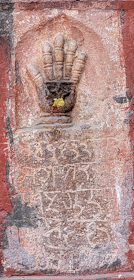
Sati was the usually forced self-immolation of widows. Sati was the tradition in India that involved widows being forced to throw themselves on their husband’s burning funeral pyre. Sometimes, they did it apparently voluntarily. It was a tradition often practised by Rajputs, but not restricted to them. During the British occupation of India, there were various attempts to outlaw sati, but incidences of it continued into the 20th century. Finally, in 1987, the Government of India passed an Act criminalising the practice of sati and its glorification.
Returning to the hands at the Junagarh Fort, one of the officials guides told us the following. Prior to being caste onto her spouse’s funeral pyre, the noble Rajput widow would dress in her finest clothes and jewellery, and approach the Daulat gate. By this time, her hands would have been covered with henna (mehndi). She would then press the palm and digits of her right hand on a stone slab, leaving a print of her hand on it. Later, an artisan carefully carved a three-dimensional impression of the widow’s hand. By that time, the poor woman had been incinerated.
In Rajasthan, various of the Princely States abolished sati in the first half of the 19th century. In Bikaner, the last Maharani to die on her husband’s pyre was in about 1825, so we were told by the guide at the fort.
My eye was immediately attracted to the sati memorials. I wonder how many other visitors to the Junagarh Fort stop and contemplate these tragic memorials before proceeding with taking photographs of each other at the many picturesque spots within the fort.


